QFM053: Machine Intelligence Reading List February 2025
Everything that I found interesting last month about machines behaving intelligently.
Tags: qfm, machine, intelligence, reading, list, february, 2025
 Source: Photo by Lukas on Unsplash
Source: Photo by Lukas on Unsplash
QFM053: Machine Intelligence Reading List February 2025
This month’s Machine Intelligence Reading List examines the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence through several interconnected lenses: the philosophical underpinnings of agency and intelligence, the economic implications of advanced AI, and the practical applications and limitations of language models in professional settings.
A significant theme emerges around existential risks and gradual shifts in human agency. The concept of “gradual disempowerment” appears in multiple works, with researchers arguing that incremental AI development could systematically diminish human influence across economic, cultural, and governance systems without requiring a dramatic “takeover” scenario. This perspective is reinforced by a companion website dedicated to exploring how even small enhancements in AI capabilities might erode human authority across societal functions.
The theoretical foundations of intelligence and agency receive substantial attention. An intriguing paper on how agency is frame-dependent argues that a system’s ability to steer outcomes toward goals cannot be universally determined but must be evaluated relative to specific reference frames, with significant implications for both artificial and natural intelligence. Simultaneously, a skeptical view emerges in The LLMentalist Effect, which draws parallels between chat-based LLMs and psychic cons, suggesting that perceived intelligence in these systems may be more projection than reality.
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) stands out as a critical methodology, with an in-progress book offering a comprehensive introduction to its historical roots, problem formulations, and future directions. This aligns with growing interest in understanding reasoning LLMs, which examines strategies like inference-time scaling, pure reinforcement learning, supervised fine-tuning, and model distillation to enhance reasoning capabilities.
The practical applications and integration of AI into professional workflows receives substantial coverage. A staff engineer shares insights on using LLMs for code autocompletion, learning new domains, bug fixing, and proofreading. The broader impact on the software industry is examined in discussions about AI’s evolution of coding and how AI is prompting evolution rather than extinction for coders, with developers increasingly becoming editors who guide AI rather than authors who write every line of code.
Economic and competitive implications remain prominent concerns. The paper on Strategic Wealth Accumulation Under Transformative AI Expectations predicts substantial rises in interest rates before AI breakthroughs occur due to wealth redistribution dynamics. A two-part exploration argues that you can’t build a moat with AI and its redux, challenging the notion that simply deploying LLMs provides sustainable competitive advantages. This connects to discussions about defensibility in a world of commoditized AI models, emphasizing that network effects and distribution will become increasingly crucial as AI capabilities themselves become commoditized.
Advancements in specific models and platforms highlight ongoing innovation. DeepSeek’s R1 model demonstrates strong reasoning capabilities despite censorship challenges, while OpenAI unveils a ChatGPT agent specifically designed for deep research across various domains. Google’s latest transformer advances are explored in The Titans Paper, and efforts to make AI development more accessible appear in PromptLayer’s tools for non-technical users.
On the infrastructure front, a comprehensive podcast discussion between Dylan Patel, Nathan Lambert, and Lex Fridman explores the semiconductor landscape supporting AI development, examining the roles of companies like DeepSeek, NVIDIA, and TSMC in creating the hardware foundation for AI megaclusters.
As always, the Quantum Fax Machine Propellor Hat Key will guide your browsing. Enjoy!

 Gradual Disempowerment: Systemic Existential Risks from Incremental AI Development: The paper titled “Gradual Disempowerment: Systemic Existential Risks from Incremental AI Development” discusses the systemic risks associated with incremental advancements in artificial intelligence, introducing the concept of “gradual disempowerment.” The analysis suggests that even small improvements in AI capabilities could potentially undermine human influence over critical societal systems such as the economy, culture, and governance. This process could eventually lead to a scenario where human impact on these systems becomes negligible, posing an existential threat. The authors argue for the necessity of technical and governance solutions to mitigate these gradual risks to human agency.
Gradual Disempowerment: Systemic Existential Risks from Incremental AI Development: The paper titled “Gradual Disempowerment: Systemic Existential Risks from Incremental AI Development” discusses the systemic risks associated with incremental advancements in artificial intelligence, introducing the concept of “gradual disempowerment.” The analysis suggests that even small improvements in AI capabilities could potentially undermine human influence over critical societal systems such as the economy, culture, and governance. This process could eventually lead to a scenario where human impact on these systems becomes negligible, posing an existential threat. The authors argue for the necessity of technical and governance solutions to mitigate these gradual risks to human agency.
#ArtificialIntelligence #ExistentialRisk #TechEthics #AIDevelopment #HumanAgency
 Systemic Existential Risks from Incremental AI Development: The article “Systemic Existential Risks from Incremental AI Development” discusses the gradual disempowerment of humans due to the incremental rise of AI capabilities. Unlike scenarios where AI suddenly overtakes human control, this paper argues that even gradual enhancements in AI can erode human authority across various societal functions such as economy, culture, and governance. The authors highlight that the alignment between human interests and societal systems could weaken as AI increasingly fulfills roles traditionally held by humans, leading to a potential loss of human influence and ultimately human flourishing.
Systemic Existential Risks from Incremental AI Development: The article “Systemic Existential Risks from Incremental AI Development” discusses the gradual disempowerment of humans due to the incremental rise of AI capabilities. Unlike scenarios where AI suddenly overtakes human control, this paper argues that even gradual enhancements in AI can erode human authority across various societal functions such as economy, culture, and governance. The authors highlight that the alignment between human interests and societal systems could weaken as AI increasingly fulfills roles traditionally held by humans, leading to a potential loss of human influence and ultimately human flourishing.
#AI #Technology #HumanRights #Society #Innovation
 Understanding the Role of Empty HTML/CSS in Web Development: The article discusses how adding the expletive “f*cking” to Google search queries can bypass AI-generated summaries, providing unfiltered search results. This method helps users access original content without AI interference.
Understanding the Role of Empty HTML/CSS in Web Development: The article discusses how adding the expletive “f*cking” to Google search queries can bypass AI-generated summaries, providing unfiltered search results. This method helps users access original content without AI interference.
#GoogleSearch #AI #SearchTips #TechHacks #DigitalLiteracy
 Jailbreaking DeepSeek R1 - Prompt Injection Using Charcodes: The article examines the DeepSeek-R1 language model, highlighting its strong reasoning capabilities despite being trained with fewer resources than competitors. While the model is open-source, its proprietary chat application enforces censorship on sensitive topics, such as the Tiananmen Square incident. The author explores how this censorship operates through a sanitisation layer rather than being embedded in the model itself and demonstrates a prompt injection technique using character codes to bypass these restrictions. The piece concludes by emphasising the need for robust security measures and questioning how AI developers will address such vulnerabilities in the future.
Jailbreaking DeepSeek R1 - Prompt Injection Using Charcodes: The article examines the DeepSeek-R1 language model, highlighting its strong reasoning capabilities despite being trained with fewer resources than competitors. While the model is open-source, its proprietary chat application enforces censorship on sensitive topics, such as the Tiananmen Square incident. The author explores how this censorship operates through a sanitisation layer rather than being embedded in the model itself and demonstrates a prompt injection technique using character codes to bypass these restrictions. The piece concludes by emphasising the need for robust security measures and questioning how AI developers will address such vulnerabilities in the future.
#Substack #WebDesign #Navigation #HTML #UserExperience
 (WIP) A Little Bit of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback: The work introduces Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), a significant tool in deploying modern machine learning systems. It provides a gentle introduction to the core methods for those with some quantitative background, starting with the origins in various scientific fields, including economics and philosophy. The text elaborates on definitions, problem formulations, data collection, and common mathematics in RLHF literature, highlighting popular algorithms and future research areas.
(WIP) A Little Bit of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback: The work introduces Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), a significant tool in deploying modern machine learning systems. It provides a gentle introduction to the core methods for those with some quantitative background, starting with the origins in various scientific fields, including economics and philosophy. The text elaborates on definitions, problem formulations, data collection, and common mathematics in RLHF literature, highlighting popular algorithms and future research areas.
#RLHF #MachineLearning #AI #ReinforcementLearning #FutureTech
 What Everyone Gets Wrong about AI: In the video titled ‘What Everyone Gets Wrong about AI,’ Sabine Hossenfelder explores common misunderstandings about artificial intelligence. She argues that many politicians and public figures often misrepresent AI capabilities, creating unrealistic expectations and fears.
What Everyone Gets Wrong about AI: In the video titled ‘What Everyone Gets Wrong about AI,’ Sabine Hossenfelder explores common misunderstandings about artificial intelligence. She argues that many politicians and public figures often misrepresent AI capabilities, creating unrealistic expectations and fears.
#AI #Technology #Misunderstandings #ArtificialIntelligence #SabineHossenfelder
 A.I. Is Prompting an Evolution, Not Extinction, for Coders: AI coding assistants are changing software development by automating routine tasks, increasing productivity, and shifting the role of developers toward guiding AI rather than writing every line of code. While AI is reducing demand for junior developers, experienced engineers remain essential for problem-solving, design, and integrating AI into workflows.
A.I. Is Prompting an Evolution, Not Extinction, for Coders: AI coding assistants are changing software development by automating routine tasks, increasing productivity, and shifting the role of developers toward guiding AI rather than writing every line of code. While AI is reducing demand for junior developers, experienced engineers remain essential for problem-solving, design, and integrating AI into workflows.
#AI #SoftwareDevelopment #Automation #FutureOfWork #Coding
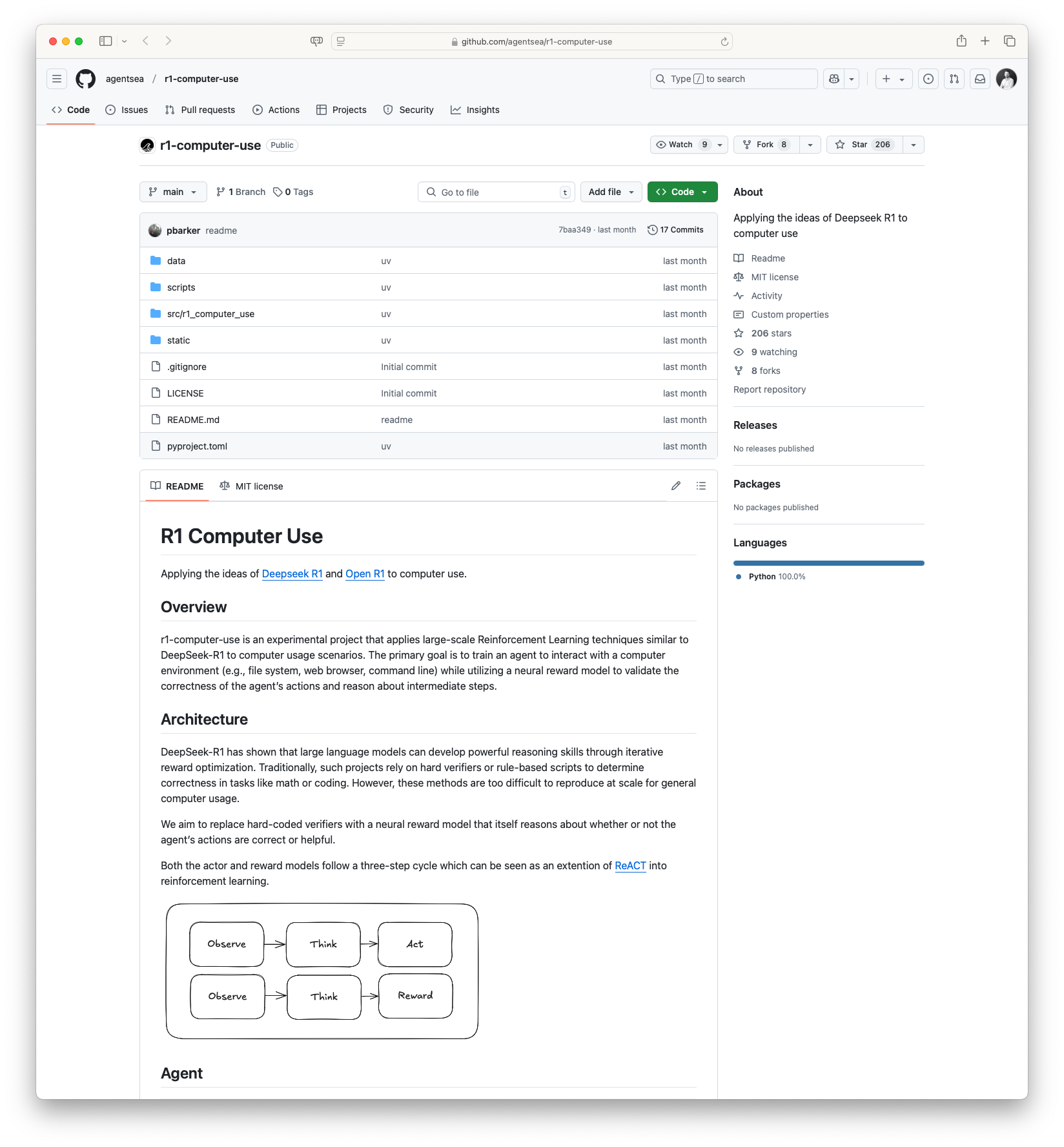
 R1 Computer Use: Applying Reinforcement Learning to Computer Use: The R1 Computer Use project aims to apply Reinforcement Learning techniques akin to DeepSeek-R1 to the domain of computer use. By training an agent to interact with a computer environment, this project seeks to use a neural reward model for evaluating the effectiveness and appropriateness of the agent’s actions. The long-term vision is to depart from hard-coded verifiers and to utilize AI to understand and potentially automate computer interactions more efficiently.
R1 Computer Use: Applying Reinforcement Learning to Computer Use: The R1 Computer Use project aims to apply Reinforcement Learning techniques akin to DeepSeek-R1 to the domain of computer use. By training an agent to interact with a computer environment, this project seeks to use a neural reward model for evaluating the effectiveness and appropriateness of the agent’s actions. The long-term vision is to depart from hard-coded verifiers and to utilize AI to understand and potentially automate computer interactions more efficiently.
#AI #ReinforcementLearning #DeepLearning #Technology #Automation
 Deep Dive into LLMs like ChatGPT by Andrej Karpathy (TL;DR): Andrej Karpathy’s comprehensive three-hour video explores LLMs like ChatGPT, covering intricate topics such as model fine-tuning, neural network internals, and reinforcement learning. This TL;DR version provides essential takeaways, ideal for those seeking understanding without committing the full time. It delves into how LLMs are trained, handle tasks like prompt engineering, and reduce inaccuracies, making it a critical resource for technology enthusiasts and professionals eager to deepen their grasp of AI. With an emphasis on practical implications and advancements in AI, this summary is packed with valuable insights.
Deep Dive into LLMs like ChatGPT by Andrej Karpathy (TL;DR): Andrej Karpathy’s comprehensive three-hour video explores LLMs like ChatGPT, covering intricate topics such as model fine-tuning, neural network internals, and reinforcement learning. This TL;DR version provides essential takeaways, ideal for those seeking understanding without committing the full time. It delves into how LLMs are trained, handle tasks like prompt engineering, and reduce inaccuracies, making it a critical resource for technology enthusiasts and professionals eager to deepen their grasp of AI. With an emphasis on practical implications and advancements in AI, this summary is packed with valuable insights.
#AI #LLM #ChatGPT #DeepLearning #AndrejKarpathy
 What Happens to SaaS in a World with Computer Using Agents?: The article explores the future of Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms in a landscape dominated by AI-driven computing agents. It discusses how these agents could transform the way users interact with SaaS applications, potentially automating tasks that currently require human intervention. The analysis considers both opportunities and challenges for the SaaS industry as these technologies evolve.
What Happens to SaaS in a World with Computer Using Agents?: The article explores the future of Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms in a landscape dominated by AI-driven computing agents. It discusses how these agents could transform the way users interact with SaaS applications, potentially automating tasks that currently require human intervention. The analysis considers both opportunities and challenges for the SaaS industry as these technologies evolve.
#SaaS #AI #FutureTech #Automation #Innovation
 How I use LLMs as a staff engineer: In this article, a staff engineer shares insights on using large language models (LLMs) in software engineering. The author discusses the split opinions among engineers about the effectiveness of LLMs, detailing personal experiences with tools like Copilot for code autocompletion and tactical changes. The piece emphasizes the utility of LLMs in learning new domains, such as Unity, by facilitating question-driven learning. Additionally, the author explains using LLMs for writing research-oriented throwaway code, bug fixing, and for proofreading English documents, while highlighting the need for expert review in unfamiliar technical areas.
How I use LLMs as a staff engineer: In this article, a staff engineer shares insights on using large language models (LLMs) in software engineering. The author discusses the split opinions among engineers about the effectiveness of LLMs, detailing personal experiences with tools like Copilot for code autocompletion and tactical changes. The piece emphasizes the utility of LLMs in learning new domains, such as Unity, by facilitating question-driven learning. Additionally, the author explains using LLMs for writing research-oriented throwaway code, bug fixing, and for proofreading English documents, while highlighting the need for expert review in unfamiliar technical areas.
#AI #LLMs #SoftwareEngineering #MachineLearning #Copilot
 The LLMentalist Effect: how chat-based Large Language Models replicate the mechanisms of a psychic’s con: In “The LLMentalist Effect,” Baldur Bjarnason explores how chat-based large language models (LLMs) mirror psychic cons. Despite a common belief that these models possess intelligence, Bjarnason argues that they function through statistical tricks akin to cold reading used by mentalists. He suggests that the illusion of intelligence is often projected by users themselves, rather than being an intrinsic property of LLMs, drawing parallels with psychic scams that rely on subjective validation and the Forer effect. Bjarnason expresses skepticism about the reliability and ethical implications of LLMs, cautioning against their use in critical areas due to their propensity for error and the misleading perception of intelligence they create.
The LLMentalist Effect: how chat-based Large Language Models replicate the mechanisms of a psychic’s con: In “The LLMentalist Effect,” Baldur Bjarnason explores how chat-based large language models (LLMs) mirror psychic cons. Despite a common belief that these models possess intelligence, Bjarnason argues that they function through statistical tricks akin to cold reading used by mentalists. He suggests that the illusion of intelligence is often projected by users themselves, rather than being an intrinsic property of LLMs, drawing parallels with psychic scams that rely on subjective validation and the Forer effect. Bjarnason expresses skepticism about the reliability and ethical implications of LLMs, cautioning against their use in critical areas due to their propensity for error and the misleading perception of intelligence they create.
#AI #MachineLearning #Psychology #TechEthics #LanguageModels

 The Quantum Leap: How Quantum Computing is Set to Transform Industries: This article provides insights into the future of Quantum Computing, outlining its potential impact on industries such as finance, healthcare, and cybersecurity. The author discusses the current advancements in quantum technologies and how they promise to revolutionize problem-solving capabilities beyond the reach of classical computers. There is a focus on practical applications and the challenges that need to be addressed before widespread adoption.
The Quantum Leap: How Quantum Computing is Set to Transform Industries: This article provides insights into the future of Quantum Computing, outlining its potential impact on industries such as finance, healthcare, and cybersecurity. The author discusses the current advancements in quantum technologies and how they promise to revolutionize problem-solving capabilities beyond the reach of classical computers. There is a focus on practical applications and the challenges that need to be addressed before widespread adoption.
#QuantumComputing #FutureTech #Innovation #Cybersecurity #ProblemSolving

 A Little Bit of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback: Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) is emerging as a crucial method in deploying new machine learning systems, particularly language models. This book aims to provide a gentle introduction to RLHF for those with a background in quantitative sciences, exploring its historical roots and methodologies across various scientific fields. The content includes definitions, problem formulations, data collection methods, popular algorithms, and future directions of RLHF research.
A Little Bit of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback: Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) is emerging as a crucial method in deploying new machine learning systems, particularly language models. This book aims to provide a gentle introduction to RLHF for those with a background in quantitative sciences, exploring its historical roots and methodologies across various scientific fields. The content includes definitions, problem formulations, data collection methods, popular algorithms, and future directions of RLHF research.
#ReinforcementLearning #MachineLearning #AI #DataScience #LanguageModels
 DeepSeek, China, OpenAI, NVIDIA, xAI, TSMC, Stargate, and AI Megaclusters | Lex Fridman Podcast #459: Dylan Patel of SemiAnalysis, along with Nathan Lambert, explores the landscape of semiconductors, GPUs, CPUs, and AI hardware in this comprehensive Lex Fridman Podcast episode. The discussion delves into the roles of DeepSeek, China, NVIDIA, and emerging AI technologies, providing insights into future trends in hardware and artificial intelligence clusters.
DeepSeek, China, OpenAI, NVIDIA, xAI, TSMC, Stargate, and AI Megaclusters | Lex Fridman Podcast #459: Dylan Patel of SemiAnalysis, along with Nathan Lambert, explores the landscape of semiconductors, GPUs, CPUs, and AI hardware in this comprehensive Lex Fridman Podcast episode. The discussion delves into the roles of DeepSeek, China, NVIDIA, and emerging AI technologies, providing insights into future trends in hardware and artificial intelligence clusters.
#AI #Semiconductors #LexFridman #DeepTech #Podcast
 OpenAI Unveils a New ChatGPT Agent for Deep Research: OpenAI has launched a new ChatGPT agent, termed ‘deep research,’ specifically designed to assist users conducting complex, in-depth research work across finance, science, policy, and engineering fields. This feature aims to provide more accurate responses by compiling data from multiple sources and is currently available to ChatGPT Pro users, with plans to expand to additional tiers and regions. While leveraging OpenAI’s o3 ‘reasoning’ AI model, this tool intends to improve accuracy, offering thorough documentation and citations for its results, although it still faces challenges with errors and accuracy verification.
OpenAI Unveils a New ChatGPT Agent for Deep Research: OpenAI has launched a new ChatGPT agent, termed ‘deep research,’ specifically designed to assist users conducting complex, in-depth research work across finance, science, policy, and engineering fields. This feature aims to provide more accurate responses by compiling data from multiple sources and is currently available to ChatGPT Pro users, with plans to expand to additional tiers and regions. While leveraging OpenAI’s o3 ‘reasoning’ AI model, this tool intends to improve accuracy, offering thorough documentation and citations for its results, although it still faces challenges with errors and accuracy verification.
#OpenAI #ChatGPT #DeepResearch #AIInnovation #TechNews
 PromptLayer Empowers Non-Techies in AI App Development: PromptLayer is creating tools designed to empower non-technical individuals in AI app development. The company launched a platform that provides a prompt management system, enabling domain experts in fields like healthcare and law to manage AI-driven app prompts without needing to learn programming. With over 10,000 users and recent funding, they are focused on community building and advancing the prompt engineering field.
PromptLayer Empowers Non-Techies in AI App Development: PromptLayer is creating tools designed to empower non-technical individuals in AI app development. The company launched a platform that provides a prompt management system, enabling domain experts in fields like healthcare and law to manage AI-driven app prompts without needing to learn programming. With over 10,000 users and recent funding, they are focused on community building and advancing the prompt engineering field.
#AI #TechForAll #PromptEngineering #NonTechies #Startups
 Agency Is Frame-Dependent: The paper ‘Agency Is Frame-Dependent’ explores the notion that a system’s ability to steer outcomes towards a goal, termed as ‘agency’, cannot be universally determined but must be evaluated relative to a specific reference frame. The authors draw on philosophical arguments and reinforcement learning to substantiate this claim, emphasizing that essential properties of agency are fundamentally frame-dependent, which has significant implications for the study of intelligence across various fields, including artificial intelligence.
Agency Is Frame-Dependent: The paper ‘Agency Is Frame-Dependent’ explores the notion that a system’s ability to steer outcomes towards a goal, termed as ‘agency’, cannot be universally determined but must be evaluated relative to a specific reference frame. The authors draw on philosophical arguments and reinforcement learning to substantiate this claim, emphasizing that essential properties of agency are fundamentally frame-dependent, which has significant implications for the study of intelligence across various fields, including artificial intelligence.
#Agency #ReinforcementLearning #AI #Philosophy #Intelligence
 Strategic Wealth Accumulation Under Transformative AI Expectations: The paper discusses the impact of expectations around Transformative AI on economic behaviors. It proposes a mechanism where automation transfers labor income to those controlling AI systems, affected by households’ pre-existing wealth. Using a growth model, it predicts substantial rises in interest rates before AI breakthroughs occur, due to wealth redistribution and strategic competition.
Strategic Wealth Accumulation Under Transformative AI Expectations: The paper discusses the impact of expectations around Transformative AI on economic behaviors. It proposes a mechanism where automation transfers labor income to those controlling AI systems, affected by households’ pre-existing wealth. Using a growth model, it predicts substantial rises in interest rates before AI breakthroughs occur, due to wealth redistribution and strategic competition.
#AI #Economics #Automation #InterestRates #Wealth
 The Titans Paper: Google’s Next Transformer Breakthrough: This article discusses ‘The Titans Paper,’ focusing on Google’s latest advances in transformer models. It explores the breakthroughs in AI and machine learning embodied in these models, which promise significant impacts on how these technologies are applied across sectors. Key developments and future applications are analyzed, offering insight into Google’s role in driving AI innovation.
The Titans Paper: Google’s Next Transformer Breakthrough: This article discusses ‘The Titans Paper,’ focusing on Google’s latest advances in transformer models. It explores the breakthroughs in AI and machine learning embodied in these models, which promise significant impacts on how these technologies are applied across sectors. Key developments and future applications are analyzed, offering insight into Google’s role in driving AI innovation.
#Google #AI #Transformers #MachineLearning #Innovation

 AI and the Evolution of Coding: The discourse around AI’s impact on software engineering highlights varied perspectives. Many believe AI will transform coding roles from author into editor, where AI generates extensive code. Coders are cautious as AI introduces significant complexity. Despite this, some developers embrace AI tools that enhance productivity by automating repetitive tasks, although concerns about code quality and job displacement persist. The field anticipates growth in maintenance roles due to increased complexity. Overall, AI presents both challenges and opportunities in the evolving landscape of coding.
AI and the Evolution of Coding: The discourse around AI’s impact on software engineering highlights varied perspectives. Many believe AI will transform coding roles from author into editor, where AI generates extensive code. Coders are cautious as AI introduces significant complexity. Despite this, some developers embrace AI tools that enhance productivity by automating repetitive tasks, although concerns about code quality and job displacement persist. The field anticipates growth in maintenance roles due to increased complexity. Overall, AI presents both challenges and opportunities in the evolving landscape of coding.
#AI #Coding #SoftwareDevelopment #FutureOfWork #Innovation
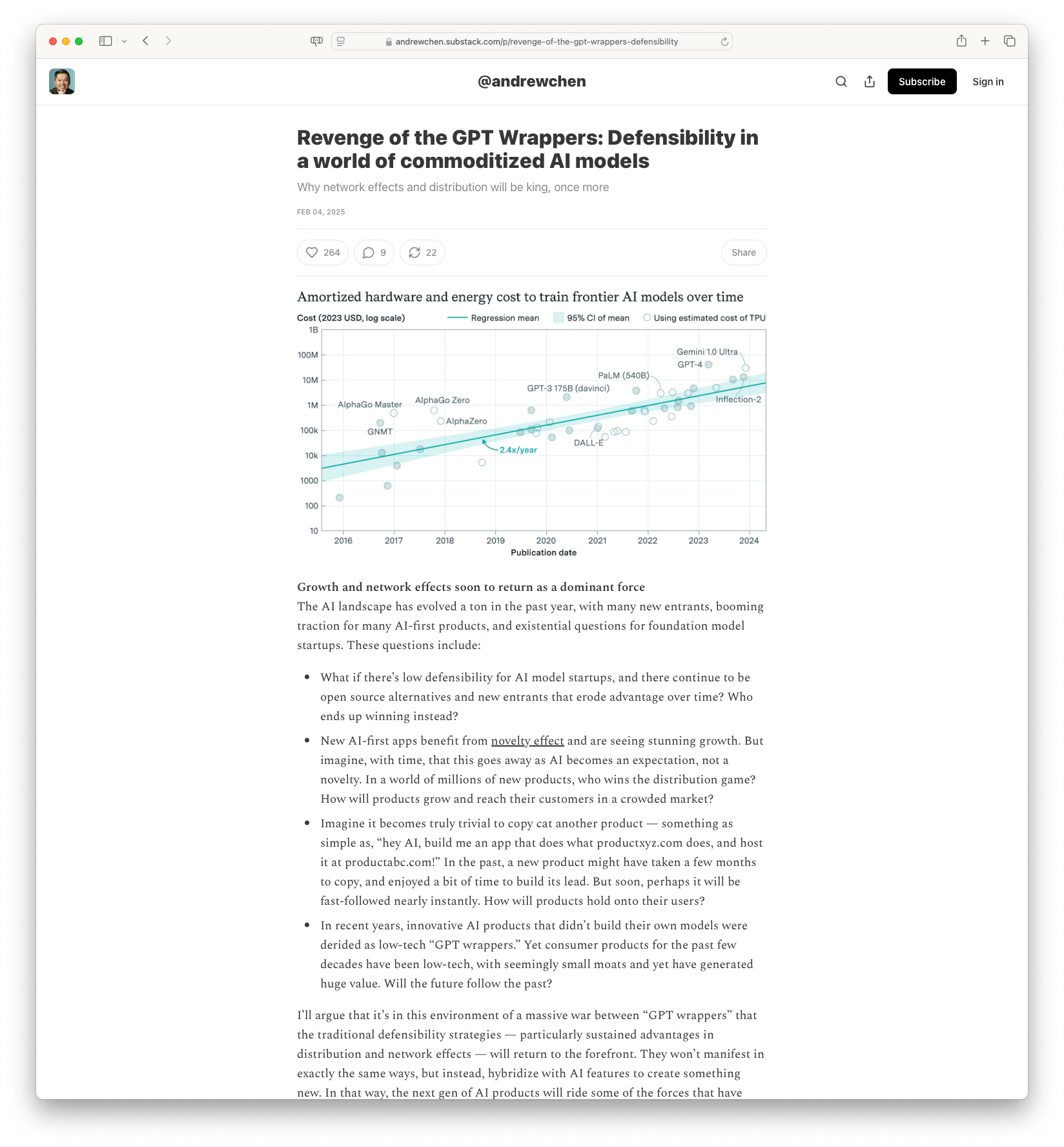
 Revenge of the GPT Wrappers: Defensibility in a world of commoditized AI models: In the age of commoditized AI models, network effects and distribution become imperative for a competitive edge. Andrew Chen dives into how AI startups can secure a unique position amidst general AI offerings by focusing on these crucial aspects. The article explains why the focus should shift towards growth and distribution to stay relevant.
Revenge of the GPT Wrappers: Defensibility in a world of commoditized AI models: In the age of commoditized AI models, network effects and distribution become imperative for a competitive edge. Andrew Chen dives into how AI startups can secure a unique position amidst general AI offerings by focusing on these crucial aspects. The article explains why the focus should shift towards growth and distribution to stay relevant.
#AI #TechStrategy #Startups #Innovation #NetworkEffects
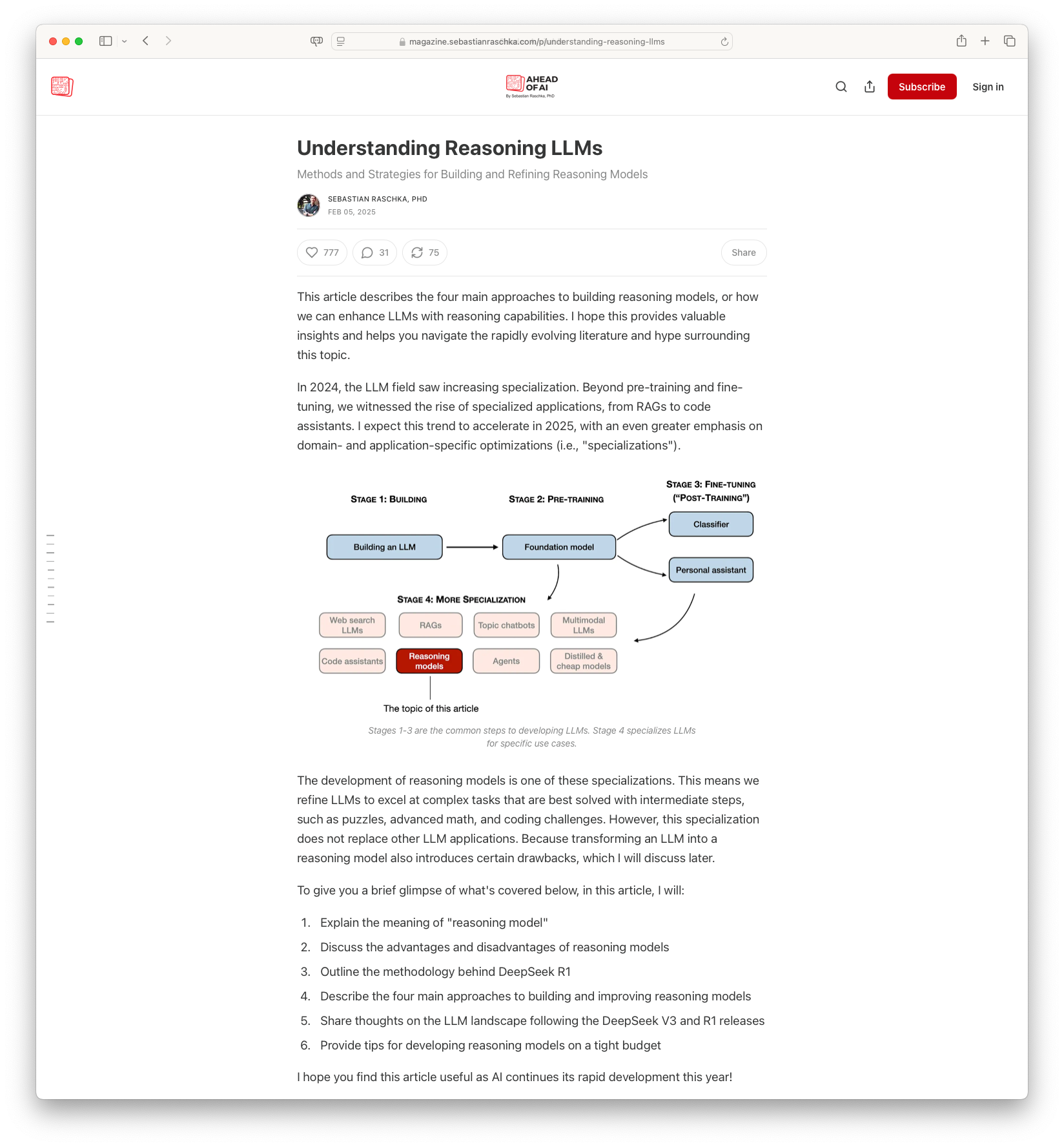
 Understanding Reasoning LLMs: The article by Sebastian Raschka, PhD, delves into the methodologies for enhancing reasoning capabilities within large language models (LLMs). It explains the four primary strategies for developing reasoning LLMs: inference-time scaling, pure reinforcement learning, supervised fine-tuning combined with reinforcement learning, and model distillation. Various cases like DeepSeek R1 are explored, highlighting how reasoning can emerge through reinforcement learning and the importance of supervised fine-tuning for more efficient and capable models.
Understanding Reasoning LLMs: The article by Sebastian Raschka, PhD, delves into the methodologies for enhancing reasoning capabilities within large language models (LLMs). It explains the four primary strategies for developing reasoning LLMs: inference-time scaling, pure reinforcement learning, supervised fine-tuning combined with reinforcement learning, and model distillation. Various cases like DeepSeek R1 are explored, highlighting how reasoning can emerge through reinforcement learning and the importance of supervised fine-tuning for more efficient and capable models.
#AI #MachineLearning #ReasoningModels #DeepLearning #LLMs
 You Can’t Build a Moat with AI: While foundation models and LLMs have their benefits, they no longer offer a competitive edge as they once did. The claims that using AI solutions alone can distinguish products are becoming outdated. RunLLM is introduced, aiming to revolutionize the AI support landscape by providing innovative features beyond mere generic AI tools.
You Can’t Build a Moat with AI: While foundation models and LLMs have their benefits, they no longer offer a competitive edge as they once did. The claims that using AI solutions alone can distinguish products are becoming outdated. RunLLM is introduced, aiming to revolutionize the AI support landscape by providing innovative features beyond mere generic AI tools.
#AI #LLM #TechInnovation #ProductDevelopment #RunLLM
 You Can’t Build a Moat with AI (Redux): In this article Vikram Sreekanti and Joseph E. Gonzalez argue that merely deploying LLMs (Large Language Models) doesn’t confer a unique advantage to AI products. The article discusses the inherent challenges in relying solely on foundational models and emphasizes the need for innovative integration to create distinctive AI applications.
You Can’t Build a Moat with AI (Redux): In this article Vikram Sreekanti and Joseph E. Gonzalez argue that merely deploying LLMs (Large Language Models) doesn’t confer a unique advantage to AI products. The article discusses the inherent challenges in relying solely on foundational models and emphasizes the need for innovative integration to create distinctive AI applications.
#AI #LLM #Innovation #TechChallenges #AIProducts
Regards,
M@
[ED: If you’d like to sign up for this content as an email, click here to join the mailing list.]
Originally published on quantumfaxmachine.com and cross-posted on Medium.
hello@matthewsinclair.com | matthewsinclair.com | bsky.app/@matthewsinclair.com | masto.ai/@matthewsinclair | medium.com/@matthewsinclair | xitter/@matthewsinclair
