QFM057: Machine Intelligence Reading List March 2025
Everything that I found interesting last month about machines behaving intelligently.
Tags: qfm, machine, intelligence, reading, list, march, 2025

QFM057: Machine Intelligence Reading List March 2025
This month’s Machine Intelligence Reading List examines the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence through several interconnected lenses: the philosophical underpinnings of agency and intelligence, the economic implications of advanced AI, and the practical applications and limitations of language models in professional settings.
A significant theme emerges around existential risks and gradual shifts in human agency. The concept of “gradual disempowerment” appears in multiple works, with researchers arguing that incremental AI development could systematically diminish human influence across economic, cultural, and governance systems without requiring a dramatic “takeover” scenario. This perspective is reinforced by a companion website dedicated to exploring how even small enhancements in AI capabilities might erode human authority across societal functions.
The theoretical foundations of intelligence and agency receive substantial attention. An intriguing paper on how agency is frame-dependent argues that a system’s ability to steer outcomes toward goals cannot be universally determined but must be evaluated relative to specific reference frames, with significant implications for both artificial and natural intelligence. Simultaneously, a skeptical view emerges in The LLMentalist Effect, which draws parallels between chat-based LLMs and psychic cons, suggesting that perceived intelligence in these systems may be more projection than reality.
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) stands out as a critical methodology, with an in-progress book offering a comprehensive introduction to its historical roots, problem formulations, and future directions. This aligns with growing interest in understanding reasoning LLMs, which examines strategies like inference-time scaling, pure reinforcement learning, supervised fine-tuning, and model distillation to enhance reasoning capabilities.
The practical applications and integration of AI into professional workflows receives substantial coverage. A staff engineer shares insights on using LLMs for code autocompletion, learning new domains, bug fixing, and proofreading. The broader impact on the software industry is examined in discussions about AI’s evolution of coding and how AI is prompting evolution rather than extinction for coders, with developers increasingly becoming editors who guide AI rather than authors who write every line of code.
Economic and competitive implications remain prominent concerns. The paper on Strategic Wealth Accumulation Under Transformative AI Expectations predicts substantial rises in interest rates before AI breakthroughs occur due to wealth redistribution dynamics. A two-part exploration argues that you can’t build a moat with AI and its redux, challenging the notion that simply deploying LLMs provides sustainable competitive advantages. This connects to discussions about defensibility in a world of commoditized AI models, emphasizing that network effects and distribution will become increasingly crucial as AI capabilities themselves become commoditized.
Advancements in specific models and platforms highlight ongoing innovation. DeepSeek’s R1 model demonstrates strong reasoning capabilities despite censorship challenges, while OpenAI unveils a ChatGPT agent specifically designed for deep research across various domains. Google’s latest transformer advances are explored in The Titans Paper, and efforts to make AI development more accessible appear in PromptLayer’s tools for non-technical users.
On the infrastructure front, a comprehensive podcast discussion between Dylan Patel, Nathan Lambert, and Lex Fridman explores the semiconductor landscape supporting AI development, examining the roles of companies like DeepSeek, NVIDIA, and TSMC in creating the hardware foundation for AI megaclusters.
As always, the Quantum Fax Machine Propellor Hat Key will guide your browsing. Enjoy!

 Vibe Coding and the Future of Software Engineering: The article explores the concept of ‘vibe coding’, a playful term referring to a more relaxed approach to coding where ideas are freely expressed and AI tools are heavily utilized. It discusses the mixed reactions from the tech community, highlighting fears about code quality issues and excitement about potential democratization of coding. The piece speculates on the future impact of AI in software development, suggesting that engineers will need to adapt to working alongside AI, which could democratize coding or raise concerns about quality and comprehension.
Vibe Coding and the Future of Software Engineering: The article explores the concept of ‘vibe coding’, a playful term referring to a more relaxed approach to coding where ideas are freely expressed and AI tools are heavily utilized. It discusses the mixed reactions from the tech community, highlighting fears about code quality issues and excitement about potential democratization of coding. The piece speculates on the future impact of AI in software development, suggesting that engineers will need to adapt to working alongside AI, which could democratize coding or raise concerns about quality and comprehension.
#VibeCoding #AI #SoftwareEngineering #FutureOfTech #CodingTrends
 Mayo Clinic’s secret weapon against AI hallucinations: Reverse RAG in action: Mayo Clinic is leveraging a unique reverse retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) strategy to address hallucination issues in AI, particularly in its clinical applications. By pairing AI with the CURE algorithm and vector databases, Mayo ensures data points are accurately linked back to original sources, thus enhancing the reliability of non-diagnostic use cases. This innovative approach has not only streamlined data retrieval but also sparked incredible interest across Mayo’s practice for its potential to reduce administrative burden and enhance patient care.
Mayo Clinic’s secret weapon against AI hallucinations: Reverse RAG in action: Mayo Clinic is leveraging a unique reverse retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) strategy to address hallucination issues in AI, particularly in its clinical applications. By pairing AI with the CURE algorithm and vector databases, Mayo ensures data points are accurately linked back to original sources, thus enhancing the reliability of non-diagnostic use cases. This innovative approach has not only streamlined data retrieval but also sparked incredible interest across Mayo’s practice for its potential to reduce administrative burden and enhance patient care.
#AI #Healthcare #Innovation #MayoClinic #DataScience
 AI + UX: design for intelligent interfaces: AI-enabled products rely on UX design to make complex systems usable by bridging human interaction with machine intelligence. Effective AI UX follows principles of explainability, error management, usability, and multimodal interaction to enhance trust, accessibility, and efficiency in AI-driven interfaces.
AI + UX: design for intelligent interfaces: AI-enabled products rely on UX design to make complex systems usable by bridging human interaction with machine intelligence. Effective AI UX follows principles of explainability, error management, usability, and multimodal interaction to enhance trust, accessibility, and efficiency in AI-driven interfaces.
#AI #UXDesign #HumanMachineInteraction #IntelligentInterfaces #DesignPrinciples
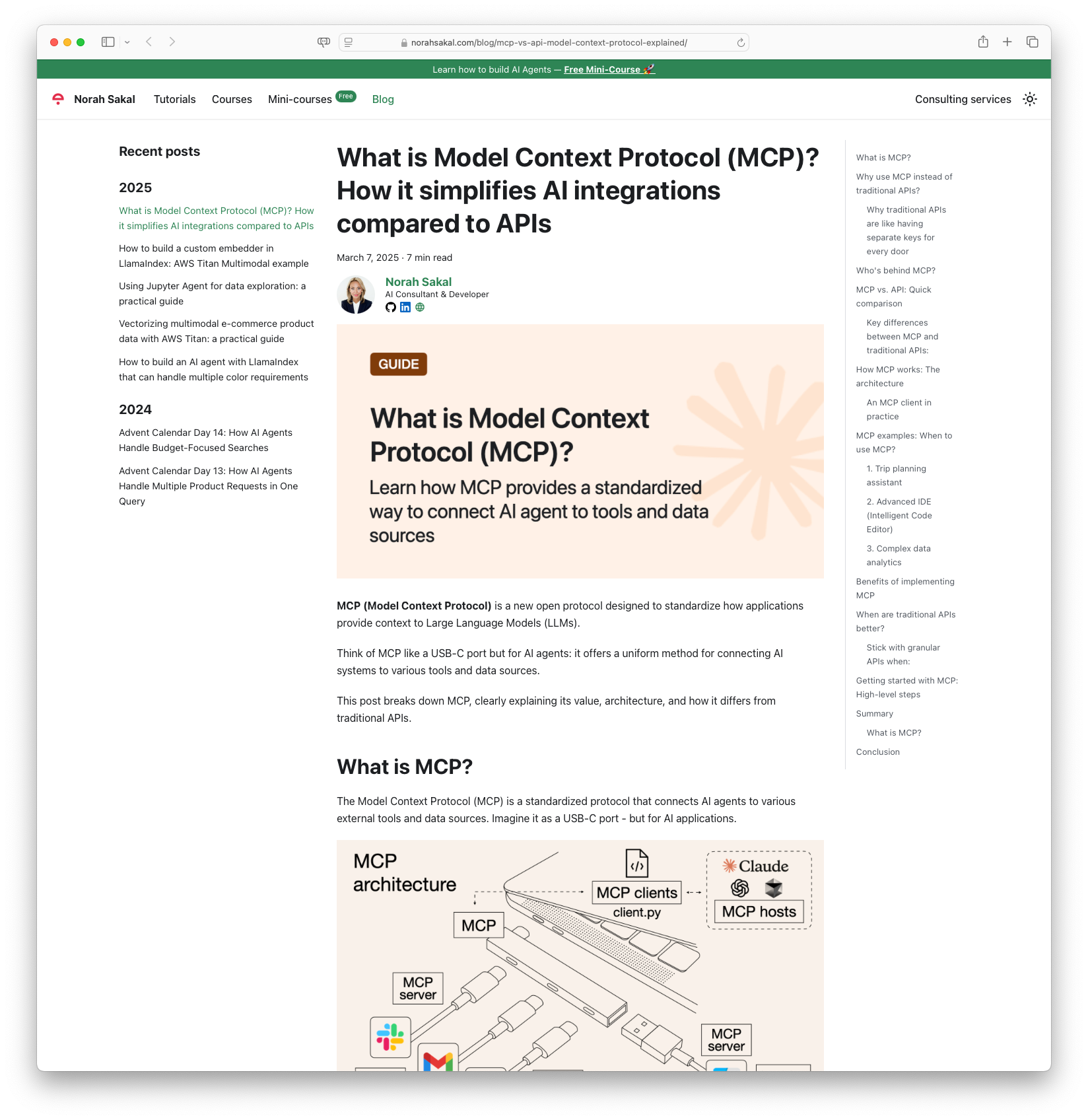
 What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)? How it simplifies AI integrations compared to APIs: The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an innovative open protocol aimed at standardizing the way applications provide context to Large Language Models (LLMs). It acts like a USB-C port for AI agents, providing a uniform method for connecting AI systems with various tools and data sources. The post by Norah Sakal highlights the advantages of using MCP over traditional APIs, such as simplifying integration processes and supporting real-time, two-way communication for AI models.
What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)? How it simplifies AI integrations compared to APIs: The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an innovative open protocol aimed at standardizing the way applications provide context to Large Language Models (LLMs). It acts like a USB-C port for AI agents, providing a uniform method for connecting AI systems with various tools and data sources. The post by Norah Sakal highlights the advantages of using MCP over traditional APIs, such as simplifying integration processes and supporting real-time, two-way communication for AI models.
#AI #MCP #APIs #AIIntegration #TechInnovation
 🔭 The Einstein AI model: In the article “The Einstein AI model,” Thomas Wolf challenges the optimistic view that AI will lead to a “compressed 21st century,” where scientific discoveries accelerate dramatically. Instead, he argues that current AI systems are akin to “yes-men on servers,” excellent at providing answers to known questions but lacking the creativity to ask groundbreaking, non-obvious questions. Wolf emphasizes the need for AI that can challenge existing knowledge and iterate new lines of inquiry, much like historical geniuses who defied conventional thinking, to truly drive scientific revolutions.
🔭 The Einstein AI model: In the article “The Einstein AI model,” Thomas Wolf challenges the optimistic view that AI will lead to a “compressed 21st century,” where scientific discoveries accelerate dramatically. Instead, he argues that current AI systems are akin to “yes-men on servers,” excellent at providing answers to known questions but lacking the creativity to ask groundbreaking, non-obvious questions. Wolf emphasizes the need for AI that can challenge existing knowledge and iterate new lines of inquiry, much like historical geniuses who defied conventional thinking, to truly drive scientific revolutions.
#AI #innovation #science #breakthrough #paradigmshift
 Machines of Loving Grace: Dario Amodei, CEO of Anthropic, discusses how AI can lead to a positive future rather than just focusing on its risks. Despite the unpredictable effects of powerful AI, Amodei presents an optimistic view of technology’s potential, with a focus on key areas such as biology, economic development, and mental health. He emphasizes the need to balance discussions of AI’s risks with its potential upsides, grounded in educated guesses about future possibilities.
Machines of Loving Grace: Dario Amodei, CEO of Anthropic, discusses how AI can lead to a positive future rather than just focusing on its risks. Despite the unpredictable effects of powerful AI, Amodei presents an optimistic view of technology’s potential, with a focus on key areas such as biology, economic development, and mental health. He emphasizes the need to balance discussions of AI’s risks with its potential upsides, grounded in educated guesses about future possibilities.
#AI #FutureTech #Innovation #MentalHealth #Biology
 The end of YC: AI-driven development tools have reduced the barriers to building software, allowing non-engineers to rapidly prototype and test ideas without traditional technical expertise. This shift challenges Silicon Valley’s model of favouring technologists over domain experts, potentially leading to a future where product success is determined more by deep industry knowledge and taste than engineering skill.
The end of YC: AI-driven development tools have reduced the barriers to building software, allowing non-engineers to rapidly prototype and test ideas without traditional technical expertise. This shift challenges Silicon Valley’s model of favouring technologists over domain experts, potentially leading to a future where product success is determined more by deep industry knowledge and taste than engineering skill.
#AI #SoftwareDevelopment #Startups #NoCode #TechDemocratisation
 The End State of the “End of Software”: The transition from coding as a niche skill to a universally accessible one is making waves in the tech world, particularly with advancements in AI and app-building platforms. The rise of technologies like Lovable and Bolt signal a shift towards democratized software creation, allowing more individuals to create and customize applications without deep technical skills. Such developments suggest a future where software becomes a medium for personal expression, akin to crafting unique content for social media, broadening the potential for innovation and creativity in technology.
The End State of the “End of Software”: The transition from coding as a niche skill to a universally accessible one is making waves in the tech world, particularly with advancements in AI and app-building platforms. The rise of technologies like Lovable and Bolt signal a shift towards democratized software creation, allowing more individuals to create and customize applications without deep technical skills. Such developments suggest a future where software becomes a medium for personal expression, akin to crafting unique content for social media, broadening the potential for innovation and creativity in technology.
#AI #SoftwareDevelopment #Innovation #TechTrends #FutureOfTech

 A Bear Case: My Predictions Regarding AI Progress: The article presents the author’s predictions on AI progress, focusing on a skeptical outlook towards current AI trends and timelines. While noting advancements like GPT-4.5, the author argues that despite improvements, there is insufficient evidence that current AI models will lead to AGI, citing diminishing returns and limitations in creative capacities. The piece explores the disparity between perceived intelligence of AI models and actual capabilities, emphasizing the distinction between hype and real-world effectiveness.
A Bear Case: My Predictions Regarding AI Progress: The article presents the author’s predictions on AI progress, focusing on a skeptical outlook towards current AI trends and timelines. While noting advancements like GPT-4.5, the author argues that despite improvements, there is insufficient evidence that current AI models will lead to AGI, citing diminishing returns and limitations in creative capacities. The piece explores the disparity between perceived intelligence of AI models and actual capabilities, emphasizing the distinction between hype and real-world effectiveness.
#AI #Predictions #AGI #GPT4 #AIAdvancements
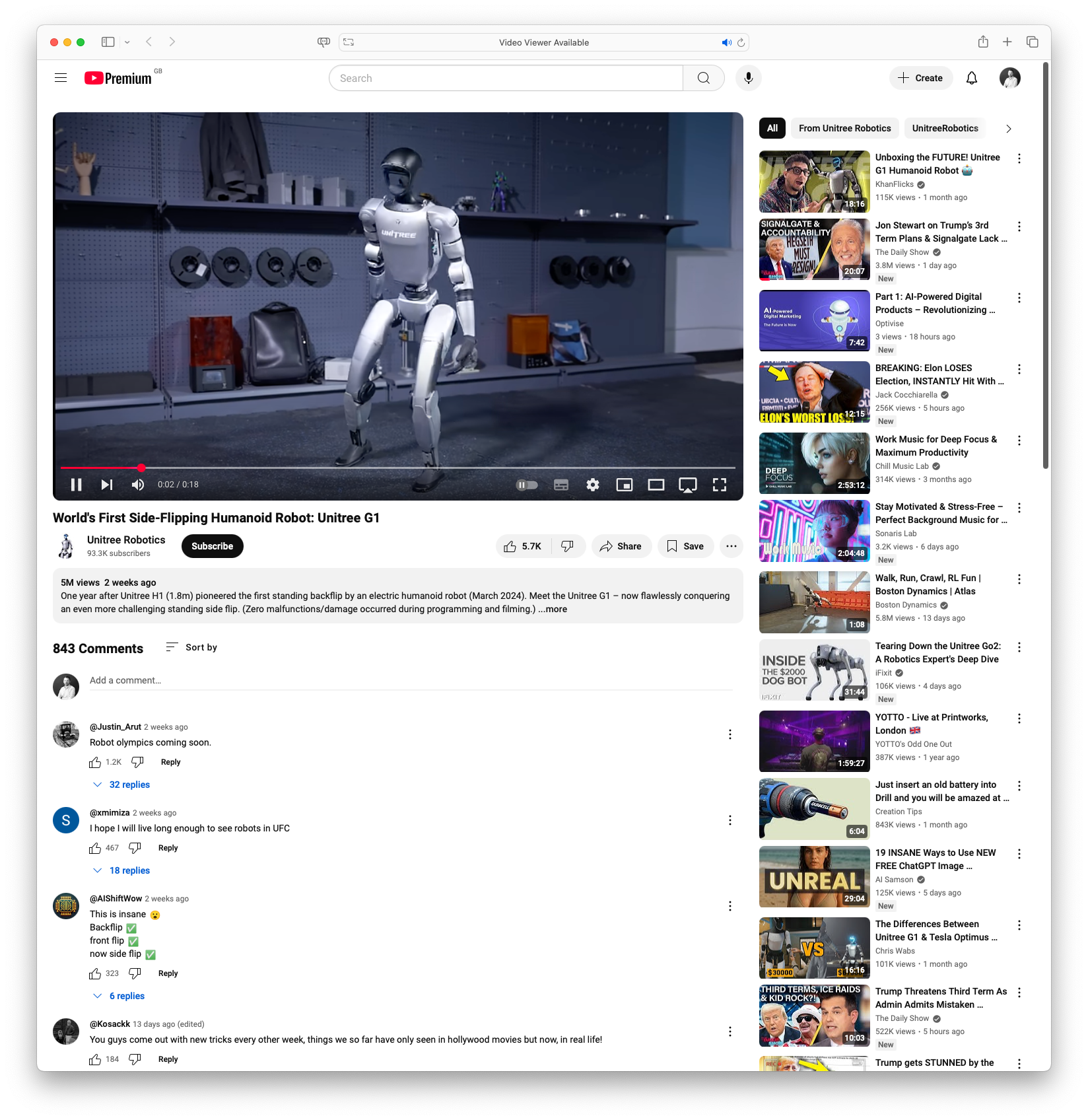
 World’s First Side-Flipping Humanoid Robot: Unitree G1: Unitree Robotics introduced the G1, the first humanoid robot capable of performing a side flip. This follows the company’s previous achievement with the Unitree H1, which was the first humanoid robot to execute a standing backflip. The G1’s design and capability mark another significant milestone in robotics, showcasing advancements in stability and agility for humanoid machines.
World’s First Side-Flipping Humanoid Robot: Unitree G1: Unitree Robotics introduced the G1, the first humanoid robot capable of performing a side flip. This follows the company’s previous achievement with the Unitree H1, which was the first humanoid robot to execute a standing backflip. The G1’s design and capability mark another significant milestone in robotics, showcasing advancements in stability and agility for humanoid machines.
#Robotics #AI #Innovation #HumanoidRobot #UnitreeG1
 VIBE CODING – The Ultimate Guide with Resources: Vibe coding is an AI-centric approach to game development that involves using natural language to generate code, promoting quick and messy prototyping that “just works.” The method was highlighted in the 2025 Vibe Coding Game Jam, where over 80% of the code needed to be AI-written. Participants had to create browser-based, login-free games, sparking innovation and experimentation among developers worldwide. This guide provides resources, tutorials, and community sites to further explore vibe coding and its potential in transforming game development.
VIBE CODING – The Ultimate Guide with Resources: Vibe coding is an AI-centric approach to game development that involves using natural language to generate code, promoting quick and messy prototyping that “just works.” The method was highlighted in the 2025 Vibe Coding Game Jam, where over 80% of the code needed to be AI-written. Participants had to create browser-based, login-free games, sparking innovation and experimentation among developers worldwide. This guide provides resources, tutorials, and community sites to further explore vibe coding and its potential in transforming game development.
#VibeCoding #AI #GameDevelopment #Innovation #TechTrends
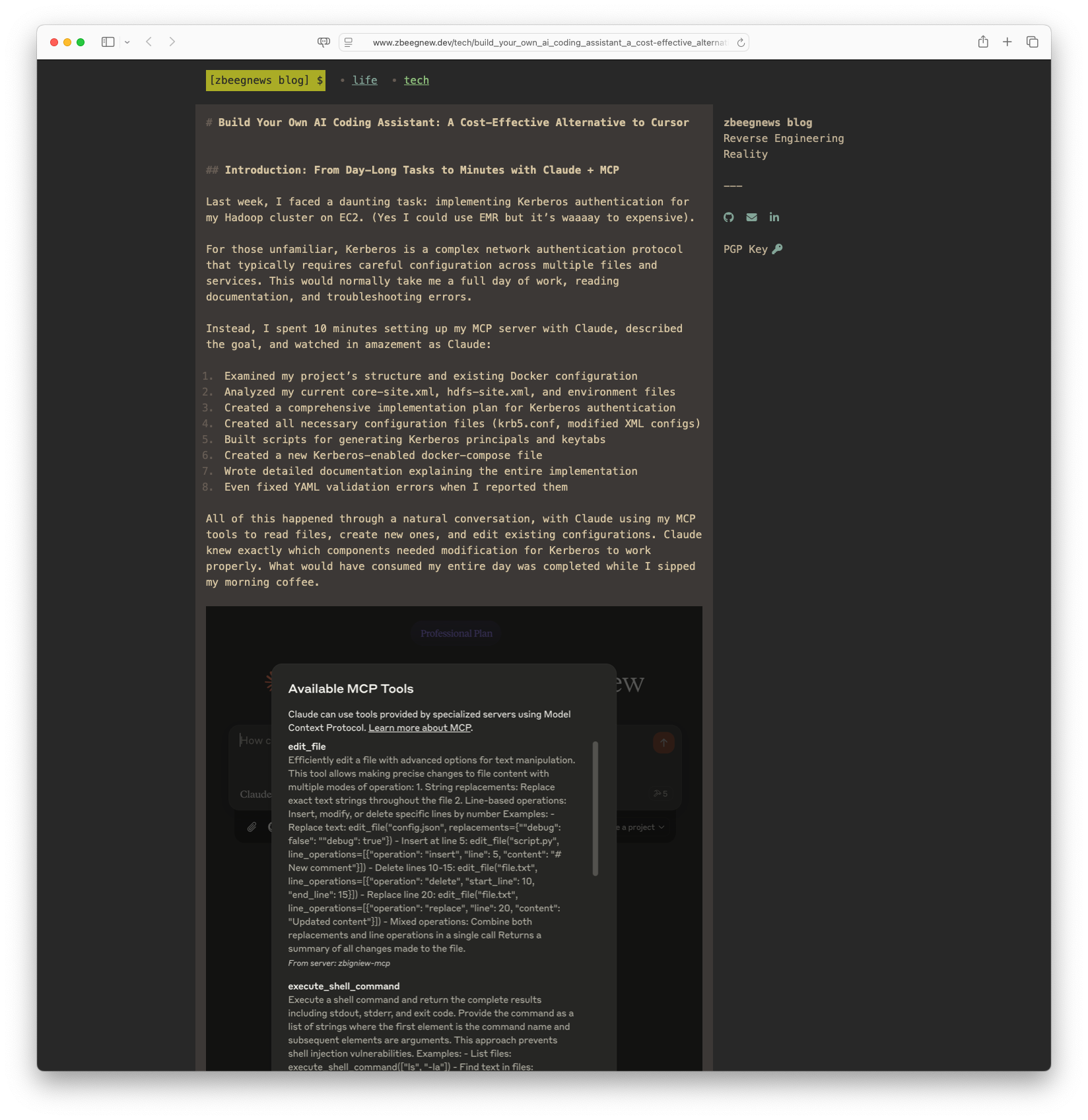
 Build Your Own AI Coding Assistant: A Cost-Effective Alternative to Cursor: The article details the author’s experience in building a custom AI coding assistant using Claude Pro and the Model Context Protocol (MCP). The author describes transforming complex tasks such as implementing Kerberos authentication for a Hadoop cluster into mere minutes, showcasing Claude’s ability to understand and automate multi-step configuration processes. The narrative highlights the cost-effectiveness and customization benefits of using MCP with an existing Claude Pro subscription compared to other commercial AI tools like Cursor, emphasizing privacy, control, and self-improvement capabilities as standout features.
Build Your Own AI Coding Assistant: A Cost-Effective Alternative to Cursor: The article details the author’s experience in building a custom AI coding assistant using Claude Pro and the Model Context Protocol (MCP). The author describes transforming complex tasks such as implementing Kerberos authentication for a Hadoop cluster into mere minutes, showcasing Claude’s ability to understand and automate multi-step configuration processes. The narrative highlights the cost-effectiveness and customization benefits of using MCP with an existing Claude Pro subscription compared to other commercial AI tools like Cursor, emphasizing privacy, control, and self-improvement capabilities as standout features.
#AIAssistant #ClaudeAI #CostEffective #CodingTools #TechInnovation
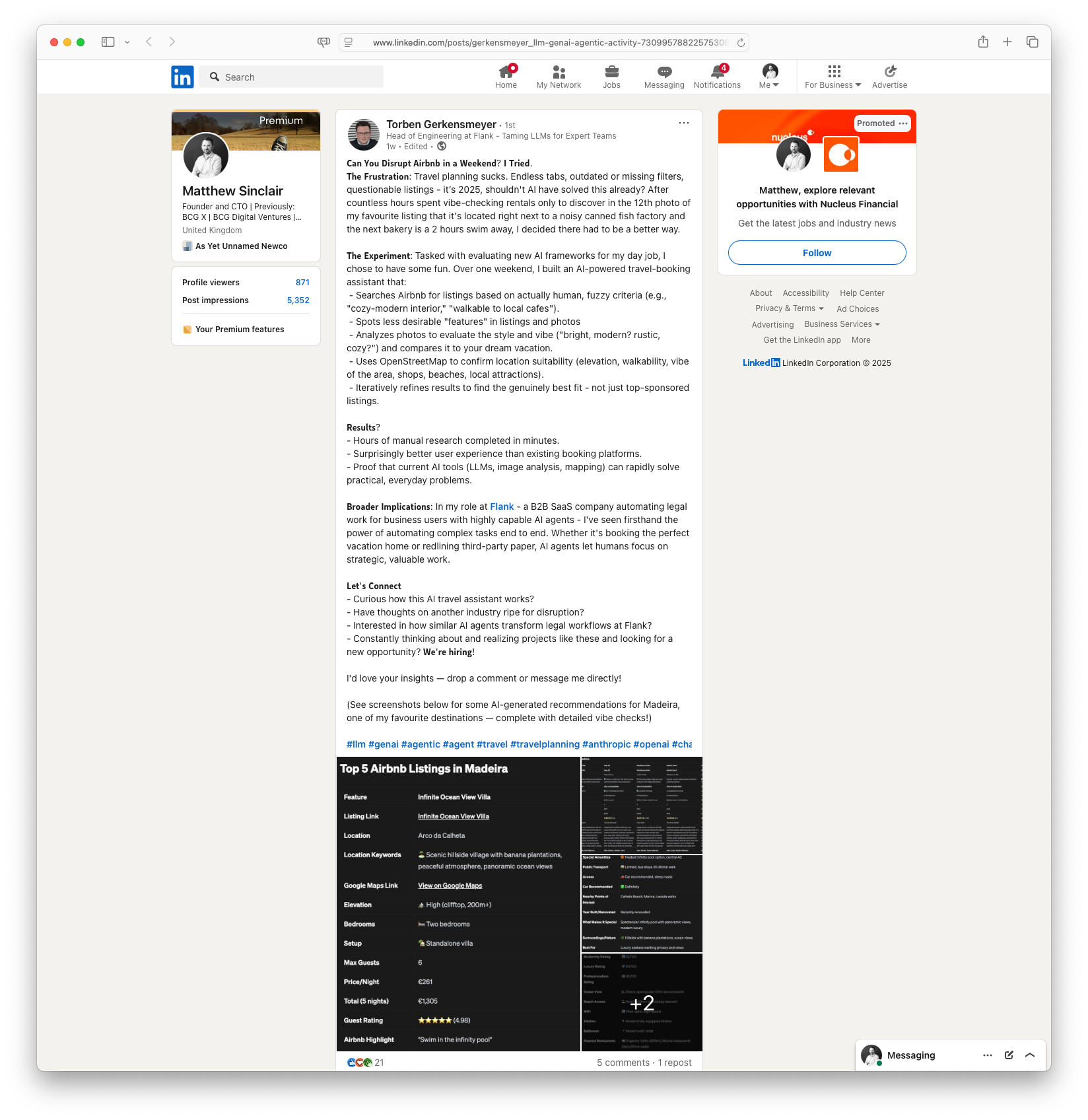
 Can you disrupt AirBnb in a Weekend?: Torben Gerkensmeyer shares his experience of developing an AI-powered travel-booking assistant over the course of a weekend. Frustrated with the existing platforms, he created a system to improve the travel planning experience by using AI tools like OpenStreetMap and image analysis to refine search results. This new assistant searches for Airbnb listings based on flexible criteria, spots unwanted features in photos, and evaluates their style and vibe, proving effective in reducing manual research time significantly.
Can you disrupt AirBnb in a Weekend?: Torben Gerkensmeyer shares his experience of developing an AI-powered travel-booking assistant over the course of a weekend. Frustrated with the existing platforms, he created a system to improve the travel planning experience by using AI tools like OpenStreetMap and image analysis to refine search results. This new assistant searches for Airbnb listings based on flexible criteria, spots unwanted features in photos, and evaluates their style and vibe, proving effective in reducing manual research time significantly.
#AI #TravelTech #WeekendProject #Innovation #LinkedIn
 AI and Economic Models: The article uses the Solow Growth Model to assess whether AI can drive long-term economic growth by increasing labour productivity through technological progress. It compares historical trends in capital and productivity to argue that while AI may boost output, its broad impact depends on complementary factors like investment, education, and adoption.
AI and Economic Models: The article uses the Solow Growth Model to assess whether AI can drive long-term economic growth by increasing labour productivity through technological progress. It compares historical trends in capital and productivity to argue that while AI may boost output, its broad impact depends on complementary factors like investment, education, and adoption.
#AI #Economics #Productivity #SolowModel #Technology
 Deep Learning is Not So Mysterious or Different: The paper argues that deep learning’s unusual generalisation behaviours—like benign overfitting and double descent—are neither unique nor mysterious, and can be explained using established frameworks such as PAC-Bayes. It proposes that soft inductive biases, which favour simpler solutions without limiting model complexity, offer a unified explanation.
Deep Learning is Not So Mysterious or Different: The paper argues that deep learning’s unusual generalisation behaviours—like benign overfitting and double descent—are neither unique nor mysterious, and can be explained using established frameworks such as PAC-Bayes. It proposes that soft inductive biases, which favour simpler solutions without limiting model complexity, offer a unified explanation.
#DeepLearning #Generalisation #PACBayes #MachineLearning #AITheory

 Hacker News discussion on ‘Deep Learning Is Not So Mysterious or Different’: The Hacker News discussion on “Deep Learning Is Not So Mysterious or Different” centres on the accessibility of deep learning concepts and the effectiveness of educational resources. Participants highlight the value of visual and intuitive explanations, such as those provided by 3Blue1Brown’s neural network series, in demystifying complex topics. The conversation also delves into the debate over whether teaching excellence stems from innate talent or dedicated effort, with opinions acknowledging the roles of both natural ability and hard work.
Hacker News discussion on ‘Deep Learning Is Not So Mysterious or Different’: The Hacker News discussion on “Deep Learning Is Not So Mysterious or Different” centres on the accessibility of deep learning concepts and the effectiveness of educational resources. Participants highlight the value of visual and intuitive explanations, such as those provided by 3Blue1Brown’s neural network series, in demystifying complex topics. The conversation also delves into the debate over whether teaching excellence stems from innate talent or dedicated effort, with opinions acknowledging the roles of both natural ability and hard work.
#DeepLearning #Education #AI #MachineLearning #Visualization
 Most AI value will come from broad automation, not from R&D: Epoch AI discusses the future economic impact of AI, arguing that AI’s main value will come from automating a wide range of labor, rather than just R&D. The article challenges the belief that AI-driven automation of R&D will be the primary driver of economic growth. It posits that automating everyday tasks will yield more economic benefits than focusing solely on scientific advancements.
Most AI value will come from broad automation, not from R&D: Epoch AI discusses the future economic impact of AI, arguing that AI’s main value will come from automating a wide range of labor, rather than just R&D. The article challenges the belief that AI-driven automation of R&D will be the primary driver of economic growth. It posits that automating everyday tasks will yield more economic benefits than focusing solely on scientific advancements.
#AI #Automation #RD #Economics #Futurism
 AI is Making Developers Dumb: The article discusses the potential downsides of using large language models (LLMs) for coding, suggesting that while LLMs can boost productivity, they may also lead to a dependency that prevents developers from deeply understanding programming concepts. It warns against the ‘Copilot Lag’—a state of over-reliance on tools like GitHub Copilot, which might diminish one’s coding skills and understanding over time. However, the piece also acknowledges that LLMs can be beneficial for learning if used critically and inquisitively, similar to a search engine, encouraging users to interrogate responses and make notes for better understanding.
AI is Making Developers Dumb: The article discusses the potential downsides of using large language models (LLMs) for coding, suggesting that while LLMs can boost productivity, they may also lead to a dependency that prevents developers from deeply understanding programming concepts. It warns against the ‘Copilot Lag’—a state of over-reliance on tools like GitHub Copilot, which might diminish one’s coding skills and understanding over time. However, the piece also acknowledges that LLMs can be beneficial for learning if used critically and inquisitively, similar to a search engine, encouraging users to interrogate responses and make notes for better understanding.
#AI #Coding #Technology #LLMs #SoftwareDevelopment
 The Bitter Lesson: Rethinking How We Build AI Systems: The article reflects on Richard Sutton’s 2019 essay, ‘The Bitter Lesson’, emphasizing the notion that sheer computational power often surpasses intricate human-designed AI systems. The author shares insights from personal experiences, advocating for AI development strategies that focus on leveraging vast computational resources rather than over-engineering processes. Examples are given from AI customer support systems, highlighting the shift from rule-based, limited compute, to scale-out solutions where extensive computational power enables the AI to uncover patterns through exploration. With the growing relevance of Reinforcement Learning (RL), the essay argues that the future of AI depends on designing scalable systems and robust learning environments that can effectively use increasing compute resources. The narrative suggests a paradigm shift for AI engineers towards optimizing computational force rather than creating rigid algorithmic structures.
The Bitter Lesson: Rethinking How We Build AI Systems: The article reflects on Richard Sutton’s 2019 essay, ‘The Bitter Lesson’, emphasizing the notion that sheer computational power often surpasses intricate human-designed AI systems. The author shares insights from personal experiences, advocating for AI development strategies that focus on leveraging vast computational resources rather than over-engineering processes. Examples are given from AI customer support systems, highlighting the shift from rule-based, limited compute, to scale-out solutions where extensive computational power enables the AI to uncover patterns through exploration. With the growing relevance of Reinforcement Learning (RL), the essay argues that the future of AI depends on designing scalable systems and robust learning environments that can effectively use increasing compute resources. The narrative suggests a paradigm shift for AI engineers towards optimizing computational force rather than creating rigid algorithmic structures.
#AI #ReinforcementLearning #Computing #MachineLearning #Innovation
Regards,
M@
[ED: If you’d like to sign up for this content as an email, click here to join the mailing list.]
Originally published on quantumfaxmachine.com and cross-posted on Medium.
hello@matthewsinclair.com | matthewsinclair.com | bsky.app/@matthewsinclair.com | masto.ai/@matthewsinclair | medium.com/@matthewsinclair | xitter/@matthewsinclair
